Last Updated on October 27, 2023 by Owen McGab Enaohwo

Featured Bonus Content: Download the FREE Quality Management System Implementation Worksheet! You will Discover Everything you need to put in place a QMS that benefits your company and customers. Click Here To Download It.
Do you have a Quality Management System your company can bank on? A stellar system that is helping you win the race against your competitors? If not, you are losing money and customers every day.
Picture this:
You have a fantastic product but your competitors are a step ahead of you. You have dedicated fans interested in buying from you, yet your competitors steal a few more away each month.
You’re left wondering what could be wrong? Your product, marketing strategy, and customer rapport are top notch. And even when you try a new approach, you don’t see a better ROI.
What if I tell you that a Quality Management System (QMS) must be put in place in your company to be able to keep your competitors on their toes? With it, you’ll be able to outline how your company wants to produce, document, control, and deliver your products and services in ways that will meet the requirements of your customers.
In this guide, I’ll be taking you through
the A-Z of Quality Management Systems (QMS), and offering an extremely valuable
worksheet that will help you implement QMS in your company.
Here’s what you’ll learn in the guide:
Quality Management System: How It All Started
People pay for and expect a quality product.
Paying customers stick with a brand because the company has proven it produces quality products and stands behind them.
To succeed in business, you need your customers to be happy with your products and thrilled to recommend them to others.
So, while your company keeps up with product innovations, it also needs to satisfy the ever-changing requirements of customers.
Enter Quality Management

“The primary focus of quality management is to meet customer requirements and to strive to exceed customer expectations.”
Quality Management System (QMS): What It Is All About
A Quality Management System (QMS) is an important process that you must put in place in your company.
A QMS basically takes a critical look at the set of policies, processes, and procedures in a company. It helps you to plan and execute the core business areas of your company such as production, development, and service.
If you want customers to always come to you for more, then make “quality management” the watchword in your company. Doing so will ensure that your products and services are consistent with your company’s goals. This will push you to maintain the desired level of excellence.
In the video below you’ll learn more about the importance of quality and why you need someone to manage this in your company.
So, how did Quality Management System (QMS) become so important?
The Rise of Quality Management Systems: What You Need To Know

According to this article, quality can be traced back to centuries ago when craftsmen began organizing into unions called guilds that people could trust to produce quality goods.
During the Industrial Revolution, workers were grouped together into factories and businesses, meaning that best practices were more important to maintain quality. During that period, the quality of a product was determined by inspection. This involved the measuring, examining, and testing of products against requirements put in place to make sure that each element followed the guidelines.
This tactic worked for a good while. However, as businesses grew and expanded, greater numbers of products were manufactured. As a result, companies experienced difficulties in following through with quality control standards, signaling the need for a change.
Enter industry experts like Deming, Dodge, Juran, and Romig who implemented these changes in the 1940s marking the beginning of Total Quality Management (TQM). With TQM, inspections were carried out by production personnel, and they did this by inspecting the products during specific production intervals. This changed the focus of quality from simply inspecting the end product to preventing end product problems by detecting them earlier in the production line.
World War II led to QMS becoming even more important. This was largely due to the mass production of military hardware – guns and bullets, vehicle parts, and so on. Military equipment needed to be checked thoroughly in order to ensure that the quality was maintained. For instance, bullets made in one state had to work with rifles made in another. During this period, the armed forces initially inspected virtually every unit of product. However, to make the process easier and also not compromise the quality, the military began to use quality techniques of sampling for inspection.
After the war, the importance of quality grew. This is because Japan enjoyed a quality revolution which improved the bad reputation it was known for in the past. It achieved this with the input of American thinkers like Juran and Deming who advised a shift in focus from inspection to improving all organizational processes. Throughout the 50s and 60s, Japan’s quality focus was on ensuring that manufacturers produced increasingly higher-quality goods at lower prices. It was during this period that Japan became the hub of quality products, beating the U.S. at their own production game, and by the 1970s, the U.S. industrial sectors such as electronics and automobiles had been broadsided by Japan’s high-quality competition.
When this happened, the American economy suffered from its inability to compete on quality with Japan. This compelled the U.S. corporate leaders to step up their game. Their response led to the birth of the concept of Total Quality Management (TQM), which set the stage for quality to flourish and operational excellence to become renowned in the U.S. With this, the management of companies and its employees were concerned about their customers, ensuring that they were satisfied and remained loyal. When independent organizations began producing standards in the late 20th century to assist in the creation and implementation of quality management systems, the phrase “Total Quality Management” began to fall out of favor, and the term “Quality Management System” or “QMS” became preferred. Hence, leading to the creation of QMS.
What a Modern QMS Does For Your Business
A well-thought-out and documented QMS will help your business immensely. These are some of the benefits that your company will derive from implementing QMS.
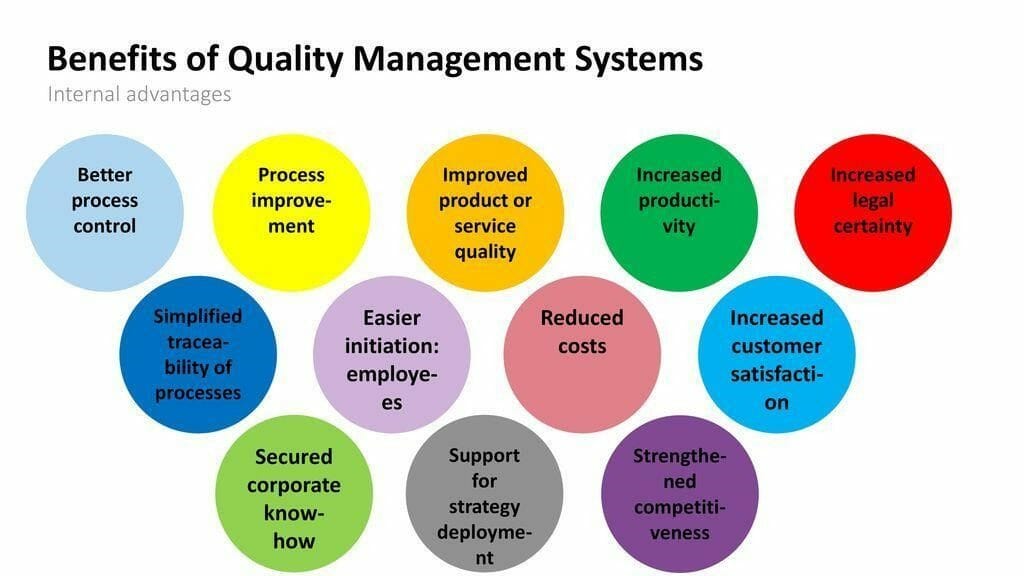
Image Credit: Dina Davidson
1. Simplify
With a QMS, you’ll be able to simplify:
- Customer requirements
- Customer satisfaction
- Your company’s processes for improvements
- Your company’s requirements in terms of effective and efficient use of resources
- Internal communication
- Prevention of product defects
When these areas are sorted, your company’s efficiency increases, making it easier for you to reach the goals you’ve set for the company’s growth.
2. Clarify
When you have a QMS in place, it will become easy to clarify the following:
- Roles and responsibilities
- Compliance with standards and regulations
- Internal processes of production/service rendering
- The path for staff training
Removing the gray areas will ensure that your employees remain focused as they won’t be confused about their roles and responsibilities and how to best serve the company.
3. Control
In addition to simplifying and clarifying, you will be able to do the following in your company with a QMS:
- Ensure your company’s commitment to its vision and mission
- Drive greater consistency in product quality
- Ensure continuous improvement
With greater control over your business, you’ll be able to document your company’s processes, procedures, and practices easily, securing greater success in the long run.
Those are the biggest benefits of the QMS, but it offers other benefits too; here’s a video for additional info.
Juran’s Quality Trilogy: What It Means For Businesses
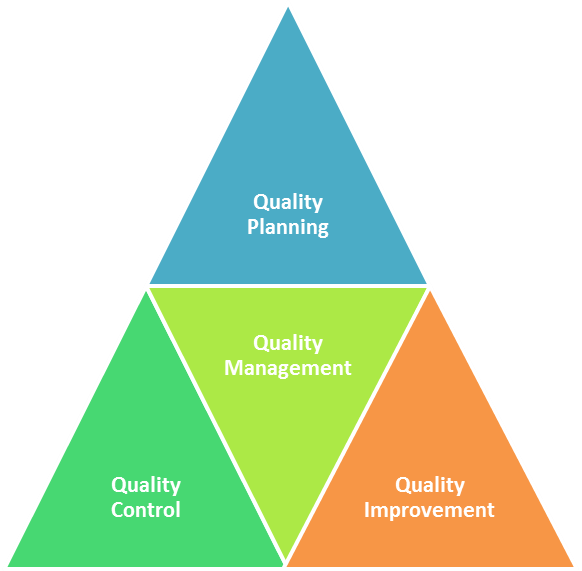
Image Credit: whatissixsigma.net
Joseph M. Juran, a management consultant, and engineer developed and wrote the quality trilogy which became famous among qualified experts.
According to him, for any company to succeed with quality management, it must have the three phases of quality planning, quality control, and quality improvement in place.
The first phase, quality planning, entails activities that must be done to adhere to the vision, mission, and goals of the company and also conform to customer and compliance requirements.
After this, the next step is to control.
The company must put in place mechanisms to ensure that everyone adheres to the quality procedure. To be able to do this, you’ll carry out periodic checks and inspections to meet the target.
Finally, there’s a need to constantly improve on the quality. So, the company must conduct adequate research to know what its customers want and satisfy them always.
This will help to identify areas for improvement from the existing performance levels and devise means and ways to achieve the new targets and implement them successfully.
Are you ready to kick off the Quality Management System (QMS) in your company?
In the next chapter, I’ll be taking you through the elements and
requirements of a QMS.
Getting Started: The Elements And Requirements Of A Quality Management System
If you want to implement any system in your company, you must understand and put in place the elements and requirements needed to achieve tremendous success. The same is applicable to a QMS.
In this chapter, I’ll be giving you a breakdown of these, so that you can build a solid foundation with it, and start the implementation process in your business on a high note.
Elements and requirements of a QMS
The elements and requirements of a QMS serve as the foundation on which the QMS in your company stands. Picture these elements and requirements as the guides which you need before you can start the implementation of a QMS in your company. These include all the activities that your company uses to direct, control, and coordinate quality. And these are designed to be applicable to any company in any industry.

1. Quality policy:
The first element of a QMS in any company is a quality policy. You need to craft a meaningful quality policy that spells out in specific terms what you mean by quality in your company. With this document, your employees and customers will know the direction of your company management with respect to quality.
2. Quality objectives:
After identifying the policy direction of quality in your company, you need to outline what you want to achieve with it.
The objectives highlight the goals for the quality of products, services, and processes. Unlike a quality policy that is set at the top level of a company, these can be specific to a department, team, process, or project. Some examples include Timeliness, Availability, Safety, and Customer Service.
3. Quality manual:
Having a quality manual in place is a no-brainer. It helps you to fully describe the scope of the QMS, and communicate what you want to achieve by emphasizing quality throughout your organization.
With it, you’ll be able to explain all the requirements of the quality standard you’re using. It is also used to describe all the QMS processes that you undergo in your company.
4. Organizational structure and responsibilities:
As stated earlier, a QMS helps in clarifying the structure of a company.
Here, you’ll highlight how your company is structured from management to the staff. Likewise, you’ll explain the responsibilities that are expected to be carried out by each person.
5. Data management:
According to Techopedia, data management refers to how an organization manages information and data for secure and structured access and storage.
It’s all about gathering, handling, transmitting, and protecting customer and company data in line with privacy laws which can vary from state to state and between countries.
6. Processes – including purchasing:
Processes are the backbone of quality management – this includes everything from best practices to safety and hygiene. You need to document everything carefully.
If an error occurs, it becomes easy for you to identify where the problem is coming from and the department in which it occurred, making it easy for you to correct it.
7. Product quality leading to customer satisfaction:
It’s only when you have a quality product that you can satisfy your customers.
With a quality product, you have a better chance of retaining your present customers.
8. Continuous improvement including corrective and preventive action:
This is about efficiency, appropriateness, managing tech changes, and so on. When mistakes occur in your process, this helps you to correct and prevent these actions. By doing this, you’ll find it easy to improve your products.
9. Quality instruments:
You need to have tools in your company that enhance the quality of your products and meet the standards of the industry.
It’s only when you have quality tools that you can produce quality products.
10. Document control:
Document control helps you to enforce controlled processes and practices within your company. It deals with the creation, review, modification, issuance, distribution, and accessibility of documents in a company.
Having a document control will help you to approve documents by ensuring that they are adequate before issuing them. You’ll also be able to update as necessary and re-approve documents if needed.
With the foundations in place, you’re on the verge of achieving amazing results. Here’s an example of what a QMS can do for you.
QMS at Work: What You Can Learn From Apple

Image Credit: chricha.com
In the U.S. and most parts of the world, the Apple brand is known for its quality. For this reason, whenever a new product is to be released from the company, thousands of users queue up in technology stores and malls to get theirs.
The reliability of Apple’s quality has enabled them to sell over 821 million iPhones in the U.S. since 2007 according to this report.
You might be wondering, why does an average technology user trust the Apple brand? How did the brand grow to become so trusted? What strategy does the company use to become dear to the hearts of users?
Of course, this didn’t happen overnight. For years, Apple invested time and resources to develop the company’s Quality Management System.
Over time, it has put in place policies that ensure the company matches its customers’ ideology. Quality, in this case, is as much about how the customer perceives the product as it is about manufacturing precision.
For instance, Apple has a procurement policy that requires the following from each of its suppliers.
- First, Apple expects its suppliers to meet the highest standards for all goods and services.
- Next, they pay close attention to the company’s culture and expectations. In this way, Apple prioritizes suppliers who look for ways to add value.
- Finally, due to the competitive and fast-paced business environment, Apple values suppliers that are innovative.
As you can see, when developing a QMS in your company, you’ll face a lot of challenges.
In the next subsection, I’ll mention the most common ones, and show you what to do to work around them.
The Biggest QMS Obstacles and How to Avoid Them
One thing is sure, you’ll encounter hurdles when developing a QMS in your company.
Here are some of the most common challenges, and what you need to do to save time and energy when encountering issues.
1. Strive for perfection:
Truth is, there’s no perfect QMS anywhere. By striving for perfection, you might get bogged down in details instead of implementing the “best possible” solution so that you have something to build on. Remember, continuous improvement is built into a QMS, so it will take place over time.
2. Unnecessary documentation:
Organizations have a lot of documents that they end up losing count of. This affects the output and productivity of the employees in the long run. However, you should note that the objective of a QMS isn’t to create paperwork, rather it is to communicate the right information appropriately. Although, if you require piles of documents in your industry, then you may need to summarize and refer to complete versions.
3. Rigid nature of QMS:
You might create a QMS that is not flexible. If it’s too hard to change a procedure in a QMS, it may not work effectively. If your QMS is like that, it will be difficult to improve when necessary. Work in flexibility to avoid it’s not helping you to achieve the best results in the future.
Since Customer requirements and companies are constantly evolving, there is a need for the QMS to evolve as well. You need to improve it from time to time so that it can keep up with the changes your company goes through. This will improve your performance and help you to seize new opportunities.

4. Lack of motivation:
Sometimes, a company decides to develop a QMS due to external factors, without carrying its staff along. When this happens, there’s usually a “them and us” atmosphere in the company. Since reluctance usually comes from fear of losing jobs, having to do more work, and retraining, it’s better to inform all members of staff and management about the next steps you want to take with your QMS. Keep everyone on board and involved to keep them motivated.
Talk to everyone involved, let them know why you must implement QMS in your company, and make sure they understand that it’s about efficiency, making their jobs easier, and getting better results.
They’ll be motivated to support it, and see it succeed.
5. Little or no attention to customers:
If you’re not careful, being focused on QMS processes instead of results will mire you in documenting and organizing, forgetting the goal of the QMS—to satisfy customers.
No level of quality is sufficient if your customers aren’t satisfied. You must invest time and resources to hear from your customers, communicate with them, and see how far you’ll go with your QMS.
In the next chapter, I’ll be introducing you to
the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), the body recognized globally for evaluating quality. The ISO sets up the quality agenda that companies
around the world follow.
Quality Standards and Methodologies: What You Need To Know About The International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
The International Organization for Standardisation (ISO) is “an independent, non-governmental international organization with a membership of 162 national standards bodies.”
The ISO gives world-class specifications for products, services, and systems, ensuring their quality, safety, and efficiency.
It officially began operations on 23rd February 1947.

Internationally, ISO 9001 is the QMS standard which many forward-thinking companies strive to meet.
How to get ISO 9001 Certified
Most companies use ISO 9001 because it’s an international standard with well-established guidelines and global acceptance.
If you’re well-prepared and understand what’s required for ISO 9001 certification, you can be done with this process within three to six months depending on your company’s size and complexity.
- The first step, which is very important, is to have an experienced person within or outside the company who knows and understands what’s needed to achieve ISO 9001 certification.
- Your expert will come up with an ISO 9001 Quality Manual instrumental for the Stage 1 audit based on the requirement set by the body. During the Stage 1 audit, an external assessor/auditor will check to be sure that your written Quality Management system meets the required ISO 9001 Standard.
- Once this is done, areas of deficiency and the expected improvement of the system will be highlighted by the auditor. Your company will be expected to make the suggested changes to qualify for the next stage.
- If this is done, you’ll then be qualified for the Stage 2 Certification Assessment. In this stage, the assessor/auditor will check to be sure that you’re working to the requirements of Quality Management Systems and the ISO 9001 Standard. This can be done by an independent 3rd party or a UKAS Accredited Certification Body.
Here are some things you must put in place in your company to achieve the ISO 9001 Certification faster.
1. A clear idea of what you stand to gain:
This is crucial. You must be sure from the outset of the objectives and benefits your company will achieve through ISO 9001 certification.
2. A documented QMS:
You need to have a QMS in place, as well as the policies and procedures required by ISO 9001.
The documentation will define the following:
- Company structure
- Who’s in charge of recording information and what information is recorded
- What is expected of employees
- How communication is done in the company
- What actions are required
- How continuity will be maintained as staff change
3. A well-defined QMS Process:
You need to define your QMS process too. However, this will be done with the necessary input from all the departments in the company.
In doing this, you will have to:
- Define who your customers are for each department. For example, your IT department’s customers include everyone in your organization using computers or other IT equipment.
- Document the activities in each area.
- Review the ISO 9001 Standard to ensure the requirements have been met.
- Identify any problem areas and rectify them.
4. Manage the documentation appropriately:
It’s necessary to communicate with all of your staff and let them know why they should keep records and use the appropriate documentation.
When you do this, you’ll be able to control the use of documents and ensure that the latest version is in use, which is important for ISO 9001 Certification.
In doing this, you’ll remove the old versions, replace them with the new ones, and distribute to the various internal departments.
This will ensure ease of access to the documents, as there will be central storage that everyone will have access to.
5. Put in place corrective and preventive measures:
It’s possible for processes to go wrong. When this happens, you need to have a system in place that fixes the problem, identify where things went wrong, then make changes to prevent these issues from happening again. In doing this, you should take note of what you did to rectify this problem.
6. Continuous support and training:
You must train your staff so that they’ll carry out their job specifications effectively. To do this, you should take note of their past experiences, education, and training. This helps them adapt to changes with new procedures and potentially new roles and responsibilities. You should also check to ensure that your staff actually read and learn these new procedures.
7. Audit your quality internally on a regular basis:
ISO does annual surveillance audits, though they recommend yearly internal audits as well (or more frequently for crucial or high-risk processes). So, you need to audit your own system internally. To do this, you may need employees within your company who are independent of the function being audited.
What the internal auditor does is to check that procedures in the quality manual are followed to the letter, and identify areas that need to be rectified.
OTHER QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (The Different Methodologies to Managing Quality):
Here are some other ways to manage quality in your company.
1. Cost of Quality (COQ):
Cost of Quality (COQ) is a QMS methodology that you can use in your company to know exactly the amount of resources that you need to prevent poor quality of your products or services. With COQ, you’ll be able to determine what your company stands to gain when it implements process improvements.
Quality-related activities that incur costs include prevention costs, appraisal costs, and internal and external failure costs.
2. Total Quality Management (TQM):
TQM is a QMS management approach that ensures that quality is emphasized throughout the entire business process. It focuses mainly on developing quality products and services on a long-term basis by highlighting each process and activity individually. By doing this, it will know those processes that contribute immensely or those that detract from the quality goals of the company.
If any process is found to be deviant, the TQM will align it with the company’s goals, values, and beliefs.
3. Kaizen:
Kaizen is a Japanese word for “improvement.” It is a QMS approach that is used for creating improvement in a company based on the idea that small, ongoing positive changes can lead to major improvements.
It was developed in the manufacturing sector to promote innovation, cut-out waste, increase productivity, and encourage worker purpose and accountability. Today, due to its numerous interpretations, other industries such as healthcare utilize it too.
4. Six Sigma:
Six Sigma is a data-driven and disciplined QMS approach which emphasizes perfection in quality. It applies specifically outlined processes to improve the business process and reduce deviation too.
Multimillion dollar companies such as Motorola and General Electric use Six Sigma as a QMS.
5. EFQM Excellence Model:
The EFQM Excellence Model (European Foundation for Quality Management) is the most widely used continuous improvement tool in the world. Any company can use it, irrespective of size or sector. What the model does is to allow companies to evaluate their current performance so that they will identify strengths as well as areas they for improvement.
Apart from internal quality improvement, it can also be used to achieve external quality recognition.
6. Corrective Action Report (CAR):
Corrective Action Report (CAR) is a QMS procedure used to initiate corrective action. It is used to respond to a defect. Simply, it’s an action carried out in the company to prevent a particular problem from occurring again.
What it does is to investigate a problem that occurred, carry out a root cause analysis using various tools, and come up with a resolution to prevent the recurrence.
For instance, CAR can be used to eliminate the cause of a detected nonconformity (when a product or service does not conform to a certain specification of the standards). While you can have more than one nonconformity, Corrective Action will be taken to prevent a said nonconformance from happening again.
7. Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI):
CQI is a QMS that is never satisfied. It lays more emphasis on the role that teams and individuals play in relation to quality. While it focuses more on the constant improvement of quality, it pays less attention to the processes and functions.
It also has a “Plan, Do, Check, Act” approach that fits into many companies and industries that have adopted it.
Depending on your company and industry, there are different QMS methodologies as stated above. Pick the one that fits your company (unless you want ISO certification) in order to evaluate quality in your company.
In the next chapter, I’ll walk you through how
to implement a QMS in your company.
The Step-by-Step Guide To Implementing a QMS In Your Organization
Having covered the basics you need to know about QMS, let’s look closely at implementing one of these systems in your company. When taking this crucial step, your aim should be to do it the right way in order to achieve great results.
In this chapter, I’ll be taking you through the seamless process of the implementation of a QMS.
Implementing A QMS: The QMS Implementation Process

The overall goal of establishing a QMS is customer satisfaction. So, if you’re implementing this system in your company, these are the steps you’ll have to follow:
1. Design:
When implementing a QMS, designing it is the first process you must carry out. Here you need to choose the methodology that suits the business, list the stakeholders, plan your timelines, decide if you’re going for (or need) a certification, and gather existing documents.
For this to be effective, you’ll have to define the structure of the QMS as mentioned previously. Then, you’ll map out a strategy that makes it easy for you to follow the implementation plan.
Similarly, you should put up all the general templates that your company plans to use for this process. For each of the templates, the procedures and instructions should include information on purpose, scope, and who is responsible for implementation.
2. Deployment:
If you already have procedures in place in your company that encompass design, you can start from this step. However, you must ensure that the procedures which you have in place are up-to-date and align with your goals and objectives.
Here, you’re talking about cloud access, printed manuals, and training. You also need to educate and enlighten your employees through a combination of documentation, education, training, tools, systems, and metrics.
If, for instance, you’re a large company operating in different countries, you might consider translating the documents into different languages.
3. Control and measure:
When controlling your QMS, you need to map your QMS documents and structure according to the established hierarchy in your company using the process/document maps and organization charts. To do this effectively, you should draft documents based on what you have in the document maps; understand your audience and address them appropriately.
On the other hand, measurement of a QMS is to determine the effectiveness and efficiency of each process towards attaining its objectives.
Some of the things you need to measure include how complete the policy definition is, what your business covers, how QMS reflects your company’s policies, where to deploy your QMS, how to use it effectively, and its relevance to the job in hand.
When measuring, you should ensure that the process used in the document control and measurement is the same as that used in the drafting process.
4. Review and Improve:
This is the final step in the QMS implementation process.
All you need to do here is review the QMS so as to communicate the findings to your employees. This step is important for your company because this is where subject matter experts from areas affected by the document scope in different departments review the documents.
When this is done, they will know which areas meet the QMS standard as outlined by the company, and those areas that need to be improved. However, if you don’t review the documents, it may result in the compliance being reduced, increase the risk of deviation from the QMS, and cause problems between staff/departments.
After reviewing the documents, it’s also important to improve what you have, based on the suggestions made by the subject matter experts in various departments. Doing this helps your company finalize and perfect your system before it’s finally subjected to the review of the regulatory bodies.
With the steps highlighted above, you’ll find it seamless to create and implement a QMS in your company.
In the next chapter, I’ll
introduce you to some principles that can make or mar the implementation of QMS
in your company.
Want to Succeed With QMS? Here Are Quality Management Principles You Must Imbue In Your Company
Quality management principles, as explained by the International Standard Organization, are a set of fundamental beliefs, norms, rules, and values that are accepted as true and can be used as a basis for quality management.
It’s a critical aspect of QMS, and its implementation or otherwise can make or mar the aims and objectives set out by your company.
In this chapter, I’ll be taking you through some quality management principles you want to ingrain in your company.
1. Customer Focus:
This is the basis for success with QMS in any company.
You must ensure that your QMS is focused on your customers, and is targeted at making them fall in love with your products.
If you’re not careful, you’ll be caught up in the QMS as a standalone project and forget the end goal.
Benefits of customer focus to your company:
- Increase in revenue and market share
- Effective use of the company’s resources to enhance customer satisfaction
- Make customers loyal to you, leading to repeat business
- Expand your customer base
- Better reputation for your company
Actions you must take to apply this principle in your company:
- Research and understand the needs of your customers and their expectations
- Communicate the needs of your customer throughout the company
- Measure the satisfaction of your customers
- Manage your company’s relationship with customers
- Ensure a balanced approach between satisfying customers and other interested parties (such as owners, employees, suppliers, financiers, local communities and society as a whole)
Image Source: StartupNation
2. Leadership:
Experienced and dedicated leaders are essential for the success of a QMS in any company.
This is because as the head of the company, you show your employees what you want them to achieve. And when they trust and admire you, you’re able to direct, drive, encourage, and show them the way.
Benefits of leadership to your company:
- Increased effectiveness and efficiency in meeting the company’s quality objectives
- Improved communication in the company between staff and management
- Better coordination of the processes in the company
- Development of the company’s ability to achieve desired results
Actions you must take to apply this principle in your company:
- Communicate the company’s mission, vision, strategy, and policies companywide
- Establish a culture of trust and integrity in the company
- Encourage the commitment of your employees to quality
- Ensure that leaders at all departments are positive examples to everyone in the company
- Inspire, encourage, and recognize people’s contribution to the growth of your company
3. Engagement
Any QMS that doesn’t involve the staff at all levels will fail sooner or later.
That is why you need to engage as many people as you can when creating and implementing a QMS in your company.
To be able to do this effectively, use and value the abilities of employees.
Benefits of engagement to your company:
- Improved understanding of the company’s quality objectives by the staff and customers
- Active involvement of employees in what you do
- Enhanced satisfaction of the stakeholders
- Increased attention to shared values and culture throughout the company
Actions you must take to apply this principle in your company:
- Conduct surveys to examine the satisfaction of customers, communicate the results, and take appropriate actions
- Communicate with employees to let them know the importance of their individual contribution
- Promote partnership throughout the company
- Facilitate open discussion in the company
4. Process Approach:
Having a process in place is necessary for the implementation of QMS to succeed within a company.
This is because, it involves all the critical aspects of a company such as managing activities as processes, deploying resources effectively and linking them to various activities, and measuring how individual activities will succeed in a company.
The process approach is a principle you must imbue in your company.
Benefits of a process approach to your company:
- Enhanced ability to focus the company’s efforts on key processes and opportunities for improvement
- Continuous and predictable outcomes through a system of aligned processes
- Optimized performance through effective process management and efficient use of resources
- Ensuring that the organization inspires confidence in interested parties
Actions you must take to apply this principle in your company:
- Define the objectives of the system and processes you must put in place to achieve them
- Understand the capabilities of your company and determine resource constraints prior to action
- Manage processes and their interrelations as a system to achieve the company’s quality objectives
- Make the necessary information available in order to operate and improve the processes
- Manage risks that can affect the overall outcomes of the QMS
5. Improvement:
You need to improve on your products on a continuous basis, for QMS to work in your company.
If you want to get this right in your company, you need to improve organizational performance and capabilities, celebrate notable improvements by your staff, and measure the improvements on a consistent basis.
Benefits of improvement to your company:
- It enhances process performance, company’s capabilities, and customer satisfaction
- It makes it easy for you to expect and react appropriately to internal and external risks
- It helps you learn more about what your customers want
- It drives you to be more innovative in your approach
Actions you must take to apply this principle in your company:
- Promote the creation of improvement objectives at all levels of the company
- Educate and train employees at all levels on how to achieve specific objectives in the company
- Ensure that people are competent to successfully promote and complete improvement projects
6. Evidence-based Decision Making:
One thing you must do when implementing a QMS in your company is you must make many decisions.
However, the best form of decisions you could make is the one which relies on verifiable facts and evidence.
Ensuring that accurate and reliable data is accessible, using appropriate methods to analyze data, making decisions based on the analysis, and ensuring that you balance it up with practical experience is the way to go in making this a reality.
Benefits of evidence-based decision making to your company:
- It enhances the decision-making processes in the company
- It improves operational effectiveness and efficiency
- It increases the ability to review, challenge, and change opinions and decisions
- It helps you demonstrate the effectiveness of past decisions
Actions you must take to apply this principle in your company:
- Make decisions and take actions based on evidence only, then balance it up with experience and intuition
- Ensure that the relevant people who need data have it
- Make sure that data and information are accurate, reliable and secure
- Improve the competence of your employees to analyze and evaluate data as needed
7. Relationship Management:
Managing relationships help you to succeed in business. This is needed even more when implementing a QMS since you’ll be working and collaborating with a lot of people.
When you manage relationships, you relate to concerned stakeholders in your company, know their fears, and attend to their needs.
Some relationship management tips include: optimizing resources, establishing long-lasting relationships with partners, and actively acknowledging your employees, suppliers, and those who make your business work.
Benefits of relationship management to your company:
- It enhances the company’s performance as it relates to interested persons and parties
- It makes it easy for interested parties to understand the company’s goals and objectives better
- It increases the capability to create value for interested parties by sharing resources and competence with them
- It provides a stable flow of goods and services through a well-supervised supply chain
Actions you must take to apply this principle in your company:
- Determine relevant interested parties (such as suppliers, partners, customers, investors, employees, and society as a whole) and their relationship to the company
- Gather and share information, expertise, and resources with relevant interested parties
- Measure the company’s performance and provide feedback to interested parties, as appropriate
- Establish the development and improvement of activities with suppliers, partners and other interested parties
- Encourage and recognize improvements and achievements by the company’s suppliers and partners
These principles can be used as a framework to guide you towards improved performance in your company.
The next chapter will take you through how the QMS works in
different industries.
How Quality Management Systems (QMS) Work In Different Industries
As mentioned previously, the QMS can be implemented in any industry.
In this chapter, I’ll explain how QMS works in different industries, and what it entails for each of them.
QMS in the Pharmaceutical Industry:
In the pharmaceutical industry, the common QMS typically relies on key regulations that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) enforces.
The big focus here is on manufacturing which includes hygiene, quality control, and adherence to FDA regulations.
It also encourages companies to take actions to correct any anomaly that arises from any of these indicators of quality in the industry.
QMS in the Automotive Industry:

ISO/TS 16949 is a Technical Specification from ISO for the automotive industry. It’s one of the most common industry-specific standards.
For any automotive company to attain this, it must specify what it requires for the design/development, production, and where relevant, installation and servicing of its products. The safety, quality of parts used, and design controls are also emphasized here.
The International Automotive Task Force (IATF) authored it, in conjunction with participating members from the private sector and regulatory agencies.
QMS in the Food Industry:

In the food industry, consideration is given to the activities that a company adheres to and risks it may encounter before a QMS can be approved.
FDA requirements, ISO quality regulations (such as ISO 22000), and similar regulatory standards of “effectiveness and efficiency” are needed to evaluate a company’s food safety quality processes.
Companies are expected to make use of the right tools and ensure they have a QMS in their company. Key issues such as food handling, packaging, cooking, distribution, and temperature controls are all checked for here.
Industries with no specific QMS:
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) uses the ISO 9001 as the standard for companies with no specific QMS.
Basically, it involves the identification of activities and tasks required to maintain the desired standard in these industries. Since these industries don’t have a specific regulation, they stand to benefit from the ISO 9001 to guarantee quality.
The hotel, hospitality, and service industries are some of those which use this standard.
QMS in the Healthcare Industry:

This is an example of the industry where only guidelines are provided. The guideline for QMS in this industry are voluntary, and not intended for certification or accreditation. Rather, it provides a framework for the design and improvement of process-based quality management systems by healthcare organizations.
The ISO guidelines for QMS in the healthcare industry are based on ISO 9004:2000, Quality management systems – Guidelines for performance improvements, and the basis for it is to ensure that the patient comes first.
Conclusion:
As important as the Quality Management System (QMS) is for every company at each growth stage, most business owners still find it difficult to implement.
They think it is an expensive marketing strategy for the likes of Apple, Samsung, and Ford. Or they believe that it’s too much work, complex, and the ROI isn’t worth it at the end of the day.
In fact, a QMS is vitally important for any company. You’ll be able to consistently:
- Meet customer requirements
- Manage internal requirements
- Manage the effective allocation of resources
Similarly, the gains of implementing this system in any company are many, which include:
- Achieve company goals
- Market your business more effectively
- Boost customer satisfaction
- Improve the availability and accuracy of documents
- Create a culture of quality
- Communicate better with your employees
- Measure the performance of individuals and teams; and
- Improve compliance
To effectively implement QMS in your company, all you need to do is follow a series of actionable steps.
First, you need to gather information about your customer requirements.
Next, document and improve your processes to meet and exceed those requirements.
Finally, you implement what you arrive at in any aspect of your business.
While implementing this system may appear a herculean task at the outset, the benefits outweigh the work involved to set up a viable QMS. The good news is that I have created this valuable QMS implementation worksheet that will walk you through the steps you must take now to implement this critical system in your business.
Download it below.

Related Posts:
Get Your Free Systemization Checklist

